Collisions in 1-D and 2-D
Collisions in 1-D and 2-D: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Collisions, Inelastic Collision, Linear Impulse and Coefficient of Restitution & Collision and Vertical Circular Motion etc.
Important Questions on Collisions in 1-D and 2-D
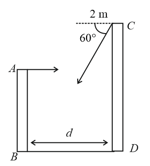
Two towers and are situated a distance apart as shown in figure. is high and is high from the ground. An object of mass is thrown from the top of horizontally with a velocity of towards . Simultaneously another object of mass is thrown from the top of at an angle of to the horizontal towards with the same magnitude of initial velocity as that of the first object. The two objects move in the same vertical plane, collide in mid-air and stick to each other. Find the position where the objects hit the ground (from ).
A moving mass of collides elastically with a stationary mass of If be the initial kinetic energy of the moving mass, the kinetic energy left with it after the collision will be :-
Two identical balls each of mass moving on straight track are approaching towards each other with same speed. Final kinetic energy of the two ball system is equal to the total energy loss during collision. is the total kinetic energy of the balls before collision and is after collision and coefficient of restitution is . Then choose the correct options
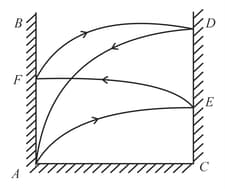
A particle is projected from the foot of one wall towards other parallel wall as shown in figure. After various collisions, finally after striking at point normally it comes back directly to the point of projection. If is the coefficient of restitution for each impact then is equal to
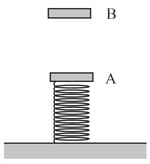
A thin plate of mass is affixed on the upper end of a spring, lower end of which is affixed on the ground. In equilibrium, the spring is compressed by an amount . Another thin plate of mass dropped from a height above plate hits the plate , moves downwards together with the plate and after reaching a lowest position, both the plates rebound upwards. What maximum height above the initial position of the plate will the plate rise?
A ball falls from a height such that it strikes the floor of lift at . If lift is moving in the upward direction with a velocity , then velocity with which the ball rebounds after elastic collision will be
A pendulum bob of mass is raised to height and released. At the bottom of its swing, it picks up a mass . To what height will the combined mass rise?
An alpha particle collides elastically with a stationary nucleus and continues moving at an angle of with respect to the original direction of motion.The nucleus recoils at an angle of with respect to this direction. Mass number of this nucleus is
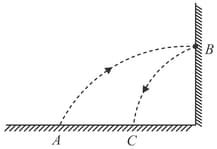
A ball is projected at an angle of with a speed of towards a wall as shown in figure. Ball rebounds such that component of its velocity perpendicular to wall reverses without change in its magnitude while the component of its velocity parallel to the wall remains same. Consider no time lapse in collision. The average acceleration (in ) of the ball throughout the motion is
There is an elastic ball which is thrown towards a rigid wall. The work done by the normal reaction exerted by the wall on the ball is:
Board is placed on board as shown. Both boards slide, without moving with respect to each other, along a frictionless horizontal surface at a speed . Board hits a resulting board "head-on". After the collision, board and stick together and board A slides on top of board and stops its motion relative to in the position shown on the diagram. What is the length (in ) of each board? AIl three boards have the same mass, size and shape. The coefficient of kinetic friction between boards and and between board and is
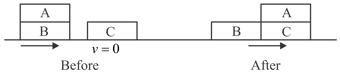
A bullet of mass is travelling with speed at an angle of with respect to the horizontal. The bullet collides with and sticks to the end of a vertical thin rod of length and mass as shown in the figure. The rod then rotates about its end which is hinged to the floor. Find (a) the angular velocity of the rod immediately after the collision and (b) the angular velocity of the rod just before when it hits the floor. Treat the bullet as a point mass.
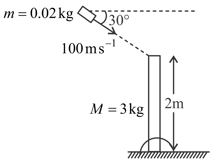
Particle is at rest and particle is moving with constant velocity as shown in diagram at . Find their velocity of separation.
A sphere of mass moving with velocity collides head on elastically with a sphere of mass at rest. After collision their respective velocities are and . The value of :
For head-on collision between two colliding balls of equal radii , the impact parameter is equal to
A particle of mass strikes another particle of same mass at rest elastically. After collision if velocity of one of the particle is , then the other must have a velocity equals to
Two identical masses are kept in contact on a smooth horizontal surface as shown. A third identical mass moving with speed hits the two balls symmetrically and comes to rest. The coefficient of restitution is
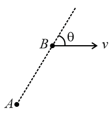
In a nuclear reactor, a neutron of high speed has to be slowed down to so that it can have a high probability of interacting with the isotope and cause it to fission. Show that fractional transferred is about when a neutron has an elastic collision with a high nuclei of deuterium. (The material making up the light nuclei, usually heavy water or graphite, is called nuclei moderator).
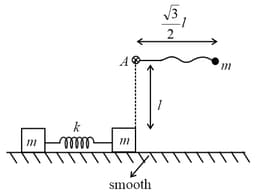
A simple pendulum of length and mass is hinged at point in a vertical plane as shown in the figure. The ball is released from the same horizontal level at a distance from point . At the lowest point bob hits a block of identical mass elastically. The maximum compression in the spring is meter. Find the value of .
(take , and ground is smooth)
A ball is dropped from height . After striking the ground time it rebounds to height . Then coefficient of restitution is
